Copper tripeptide
CAS No. 89030-95-5
Copper tripeptide( GHK-Cu )
Catalog No. M22297 CAS No. 89030-95-5
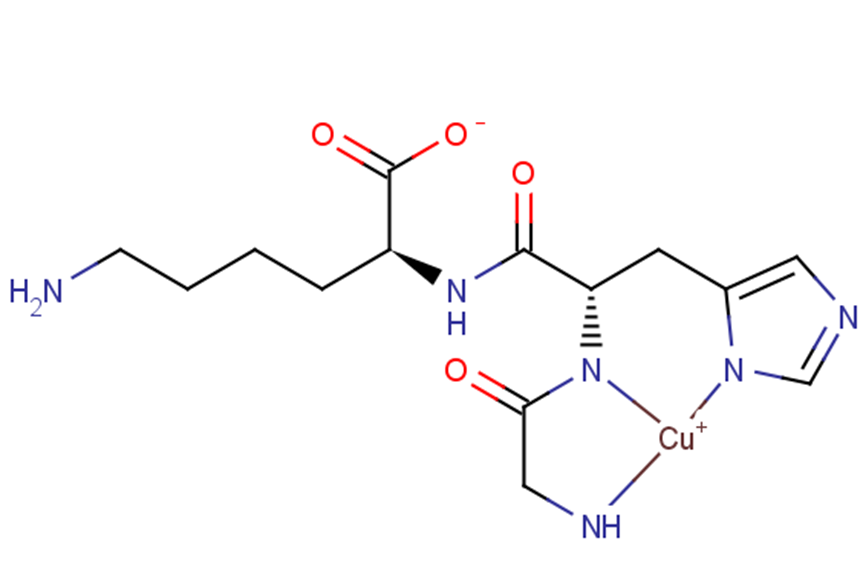
Copper peptide GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring copper complex of the tripeptide glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine. The tripeptide has strong affinity for copper(II) and was first isolated from human plasma. It can be found also in saliva and urine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 97 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCopper tripeptide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCopper peptide GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring copper complex of the tripeptide glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine. The tripeptide has strong affinity for copper(II) and was first isolated from human plasma. It can be found also in saliva and urine.
-
DescriptionCopper peptide GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring copper complex of the tripeptide glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine. The tripeptide has strong affinity for copper(II) and was first isolated from human plasma. It can be found also in saliva and urine.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsGHK-Cu
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number89030-95-5
-
Formula Weight400.9
-
Molecular FormulaC14H21CuN6O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 50 mg/mL (124.41 mM)
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Pollard JD, et al. Effects of copper tripeptide on the growth and expression of growth factors by normal and irradiated fibroblasts. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2005 Jan-Feb;7(1):27-31.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Limocitrin-3-O-rutin...
The herbs of Sedum alfredii.
-
Pentetic Acid
An iron chelating agent with properties like edetic acid. DTPA has also been used as a chelator for other metals, such as plutonium.
-
2-Iodobenzenamine
2-Iodobenzenamine is an agent of biochemical.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


